Adding Value to the Motor: Operated Valve, Part 4
The valve control market faces increasing pressure from commoditisation of its products. Here’s how to avoid a race to the bottom.

New actuator maintenance

Screen after maintenance

4 years actuator maintenance
10 year actuator maintenance
Each article focuses on a different stage of the product’s life cycle:
• Control system design and actuator specification
• Plant installation and commissioning
• Plant operation
• Maintenance and asset management.
Together, the four articles consider how an integrated control and actuator solution better satisfies customer needs and adds real customer value.
Design, specification, installation and commissioning
In the first article [Valve User, Winter 2015] we saw how the powerful control features of modern actuators bring benefits at the design stage. For example, analogue-todigital [A/D] converters built into AUMA actuators simplify control system design by avoiding the need for flow and level sensors to have their own fieldbus A/D converters. Variable-speed operation as found in the SIPOS actuator series can eliminate water hammer, reduce valve seat wear, improve emergency shutdown performance, and provide near-linear performance from lower-cost non-linear valves.
The second article [Valve User, Spring 2016] showed how actuator design features affect the ordering, installation and commissioning phases of a project. AUMA’s modular actuator concept allows the three key components to remain separate right up to installation. Wiring, programming and commissioning can overlap, saving many weeks on tight project timescales. On-site cabling becomes a plug-and-play operation. Modular assembly keeps other site work to a minimum, saving time and improving safety especially when working in confined spaces or at heights.
For the third article [Valve User, Summer 2016], we moved on to show how choosing the right actuator can benefit day-today plant operation in terms of energy efficiency, ergonomics and controllability. We looked at how a variable speed actuator such as the SIPOS 7 reduces energy, how easy programming and great ergonomics make the life of a site engineer easier, and how a data-enabled actuator can become part of the site Fieldbus system, significantly reducing data cabling costs.
In this fourth and final part, we consider the importance of predictive maintenance and asset management to maximise availability and the importance of sophisticated sensor systems in clearly identifying when an actuator requires attention, well before its process-critical operation is compromised. We also look at the opportunities presented when well trained, certificated, cardcarrying installation and maintenance engineers are available throughout the supply chain.
The three styles of maintenance
Classically, there are three styles, or levels, of maintenance: ‘Reactive’ maintenance, or the ‘fix it when it breaks’ approach, is in fact a legitimate way of dealing with equipment where the cost is relatively low, the likelihood of the equipment failing is low and the consequences of its failure are relatively insignificant. The next level up, ‘preventative’ maintenance, gives us a rigid process, where equipment is ‘serviced’ on a regular basis, with oils, greases, filters and seals replaced and everything given a clean. The advent of small, reliable sensors and the means to communicate with a central system gives us what is currently the best possible way to maintain critical components – Predictive Maintenance, where there are no defined service intervals, but the equipment itself tells us when it needs attention, and it does so in a way that makes sure that it continues reliably and efficiently doing its job.
Preventative maintenance in Actuators
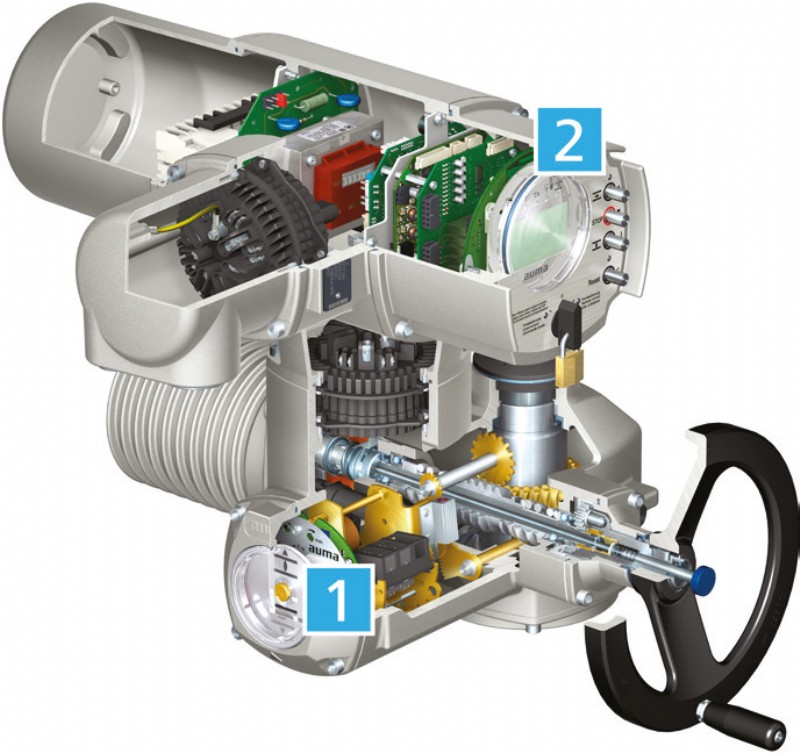
There are a number of points of attention in an electric actuator – the seals, the grease, reversing contactors and the mechanical components, and the preventative maintenance required within the system is determined by a combination of data logging and sensor measurement.
Clearly, each actuator will operate with a slightly different duty, and we can record the number of starts, the number of turns of the shaft, the time the unit has been operating and the output speed, all of which can predict when the reversing contactors and the mechanics of the actuator will require attention. We can’t directly measure the condition of the grease, but we can measure vibration, temperature and torque at various points in the actuator, and derive the machine conditions from that.
With a sophisticated set of algorithms, the AUMA actuator then continually updates its maintenance log, ready to signal an alert or alarm if any parameter reaches a defined trigger point. The actuator forms a defined control loop with the valve it operates in the system, so the conditions experienced by the actuator can also provide critical information about the process. Operators want to be managing information, not ‘lost in data’ so, for example, a preventative maintenance signal that integrates torque measurement with a differential pressure sensor can warn of a loss of flow in a pipe as well as the unlikely failure of a valve.
These sophisticated functions are not restricted to top end actuators such as the SIPOS 7, AUMA SA and SQ actuators are already supplied with the AUMA Asset Management Function as standard, the only condition being that the actuator is fitted with AUMA’s electronic control unit.
Communication for Asset Management
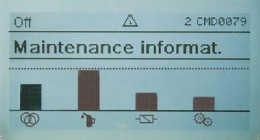
AUMA actuators feature a clear and logical control interface, which makes configuration straightforward for contractors and site staff. The maintenance information screen allows staff to see at a glance the condition of seals, grease, contactors and mechanics, and how far the condition of each has progressed towards the trigger point when attention is required.
An informed decision can be made about replacements and maintenance and, once the alarm trigger point has been reached, a signal is both displayed on the screen and communicated more widely through whichever network is in place. Fieldbus systems are well-established for actuator applications and the information derived from the algorithms could easily be shared onto the Internet of Things.
Adding value through set-up and maintenance
Vital equipment such as valve actuators should of course be maintained in line with the manufacturer’s recommendations, and major utilities are increasingly insisting that this important component of asset management should not be left to untrained staff. This is a huge opportunity for company service departments, of course, but AUMA have taken a more indepth approach. AUMA’s own in-house service operation is, of course, fully staffed, trained and equipped, but we have recognised that there are a number of points within the market where customers and supply chain partners value additional flexibility.
That recognition was the genesis of AUMA’s ACE (AUMA Certified Engineering) programme, a three stage training programme leading to certification of service technicians to empower them to work on AUMA actuators. There is a huge added value opportunity for the valve manufacturers, in mounting, testing, set up and configuration of the actuators prior to delivery to site. ACE Level 1 has been designed for just this purpose, covering the required skills for correct mounting, commissioning and testing. ACE Levels 2 and 3 are both for staff working on site, who may also need to undertake fault finding and corrective actions, with additional modules on top of those covered by Level 1 to enhance knowledge. Level 2 is aimed at staff within user and service organisations, for example technicians within water companies. Level 3 represents the level reached by AUMA’s in house team and selected partner organisations, so a Level 3 ACE Technician can be considered an expert in AUMA equipment. All ACE technicians are card-carrying, backed up with a registration that must be regularly renewed.
This fourth article has shown how the valve actuator is a vital tool within the wider topic of asset management, and how predictive maintenance and the successful delivery of that maintenance can add value for both actuator and valve manufacturer while delivering higher standards within the process for the end user.
Tel: +44(0)1275 871141
Email: mail@auma.co.uk
Web: www.auma.com

| Telephone: | 01275 871141 |
| Email: | mail.uk@auma.co.uk |
| Website: | www.auma.co.uk |
| More information on the AUMA Actuators Ltd BVAA Member Directory Page |
Search related valve / actuator articles: AUMA Actuators LtdIssue 39Electric ActuatorsMaster Class






-web.jpg)





